 Driving railway vehicles
Driving railway vehicles
- Driving rail vehicles biaxial - line 211
- Driving rail vehicles triaxial - A 314
- Driving rail vehicles quadriaxial - A 415
Special driving railway vehicles for light shunting and manipulation with railway wagons designed to ensure technological production operator onsite loading and unloading takes place. Cable shunting devices
Cable shunting devices is designed for the rail cars shunting during their loading and unloading at the sidings, filling stations of liquid products and terminals. The device is able, according to the local conditions, to put in move and to brake the rail cars set with the total weight of up to 2500 t, device PZ 15 of up to 500 tons in both directions.
Cable shunting devices
Cable shunting devices is designed for the rail cars shunting during their loading and unloading at the sidings, filling stations of liquid products and terminals. The device is able, according to the local conditions, to put in move and to brake the rail cars set with the total weight of up to 2500 t, device PZ 15 of up to 500 tons in both directions. Special equipment
Special equipment
- Dynamic manipulator HW1E
- Electromechanical Train Wheel Stopper EMVZ-02
- Rail locking mechanism KAM-60-8
The dynamic manipulator HW1E has been developed for the wagons rotary tipplers with aim to catch and stop incoming loaded wagons, their appropriate arrangement, and once they are unloaded, their pull out. An important condition is the observance of the velocity of incoming wagons, which can be guaranteed.
Electromechanical Train Wheel Stopper EMVZ-02 has been developed for places on marshalling yards and railway sidings, where the track operator regularly secures the wagons with a wheel stopper.
Rail locking mechanism KAM-60-8 is intended for locking and holding stationary railway wagons on inclined lines during operation with individual wagons.
Driving rail vehicles triaxial - A 314
The accumulator fed locomotive A 314 (710 201-5) is three-axle driving rail vehicle designed for a light duty and medium heavy duty service at the railway sidings of the industrial enterprises, logistic terminals, for assembling wagons into trains at handling track ages owned by the railway operators.
Basic description
This vehicle was developed on grounds of the extensive reconstruction and modernization of diesel-hydraulic locomotive of 710 series (the original brand mark T334) made by ČKD Lokomotivka n.p. Praha, when only the frame and driving gear were retained from the original machine. All other parts of the towing vehicle are designed as new building. The vehicle is equipped with buffing and attachment mechanisms (it can also be supplemented with pneumatically controlled automatic coupler – unnecessary presence of the shunter during the locomotive’s connecting with wagon or with wagon sets). The remote control allows for unnecessary presence of the operator in the cabin during the operation.
Design
The vehicle consists of the base frame, on which there are placed two pre-built shelves on each side (battery compartment and power electronics with pneumatic control unit) and the tower cabin for the operator. The shunters gained a safe space at the slope stairway, where they are protected by a massive front-end of the machine. The machine is equipped with required lighting and, in addition, there are 2 strobe beacons at the cabin’s roof, which are activated in each case when the remote control is selected in operation.
The cabin is fitted with large windows, retractable side windows, windshield vipers in both directions of travel. The control panels are placed diagonally in both directions of travel, with ergonomic adjustable chairs. The cabin consists of the steel frame and body made of the steel sheets. The cabin is noiseless, insulated and heated. The entry into the cabin from both sides of the stands. The main service brake of the accumulator locomotive is the electrodynamic brake (EDB), which is based upon on the very principle of the asynchronous motor, when such motor under prevailing presence of the moment from load switches itself into generative mode regardless of the operator’s will. The current generated by traction electric motor goes into changer-rectifier and subsequently back to accumulator. Thus, the phenomenon called recuperation occurs.
Technical description
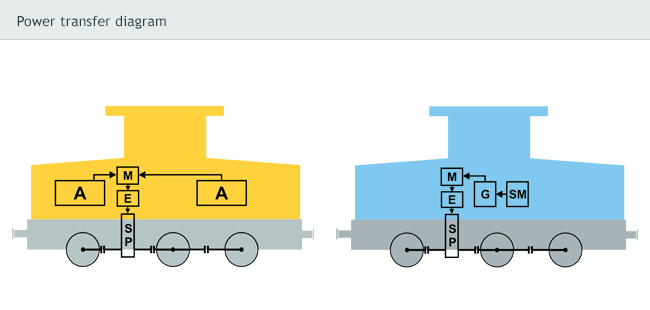
The electromechanical transfer of power is involved, where the source of electric current is traction lead accumulator with rated voltage of 720 V and capacity of 640 Ah, which is charged by the charger working on high-frequency charging principle. Any travel of the vehicle during the charging is excluded. On-board net is charging with the 24 V voltage the accumulator, which is constantly charged from the traction accumulator. The electric cable with the plug 125A to be used for connecting the charger to the 3×400 V network.
The electric current flows to the vector driven inverter and from there to externally cooled traction asynchronous squirrel-cage induction motor. The electric motor’s torque is transmitted through the clutch to the traction reduction gearbox and with the help of cardan shafts to the cabinets on the axle.
The power transfer system is controlled by a microprocessor unit, which receives feedback from the encoder (optoelectronic sensor of revolutions) built-in at the output shaft of the traction electric motor. When the operator files request for work performance, the vehicle will start its travel up the ramp of the inverter at the selected speed. Then, the controlling unit sustains the velocity independently on the slope and nature of torque from load.
Thanks to the full vector control of traction changer, it is possible to achieve high starting torque of the electric motor at very low speed. Another advantage of the traction inverter is the output frequency rising on adjustable ramp that would not allow for the motor’s any uncontrolled revolutions and, due to this, any slippage of the driving wheel sets in unfavourable adhesion conditions. The selection of the vehicle’s direction and speed is executed from two operating positions with the help of lever controller.
Benefits
- Environmental friendly operation
- Very significant operative cost reduction
- Low noise
- Easy operation
- Favourable purchase price
Driving gear
Download Type List »
Fill in the questionnaire for particular specification of the equipment »
Railway vehicles
| Questionnaire | Type List | Photo Gallery |
| Basic technical data A 314 | |
|---|---|
| Wheel Set Layout | C |
| Gauge | 1 435 mm |
| Max. Width | 2 950 mm |
| Max. Height | 4 320 mm |
| Length Across Buffers | 9 400 mm |
| Axle Length | 2 000/2 200 mm |
| Wheel Set Diameter | 1 000 mm |
| Smallest Radius of Travel Arc | 80 m |
| Total Weight | 48 t |
| Weight Per Axle | 16 t |
| Peak Output | 175 kW |
| Output Transfer | electromechanical |
| Max. Operating Velocity | 20 km/hour |
| Max. Towing Force | 158 kN |
| Continuous Towing Force | 70 kN |
| Max. Direct Track Load | 2 000 t |
| Towing Force Use Range | 0 - 7,6 km/hour |









